Payment fraud continues to be a massive problem in recent years for eCommerce merchants.
The enormous costs are measured in tremendous chargeback fees, fraud prevention efforts, and even lost merchandise.
According to a Juniper study, by the end of 2024, Ecommerce merchants may lose an estimated $24 billion due to payment fraud.
All these statistics and worries may cause you a massive headache next to all the efforts you have to deal with on a daily level.
That’s why eCommerce fraud prevention is the number one priority that can affect your business, positively or negatively – it depends on you.
Protecting your eCommerce store requires a bit of knowledge and strategy on dealing with it, your commitment, and some tools that will make your fight against fraud easier.
In this article, we’ll go through eCommerce fraud prevention best practices that you should implement to make your store secure for customers and also protect yourself.
So if you’re ready, let’s begin.
What is Ecommerce Fraud?
When it’s up to Ecommerce, we’re talking about commercial transactions over the Internet, made through an online store.
When there are online transactions, there are also frauds.
Ecommerce fraud is a criminal deception during an online transaction that intends to result in a financial or personal gain of the fraudster that negatively affects the merchant or the customer.
Ecommerce fraud is usually also named payment fraud.
When it’s up to Ecommerce fraud, the target is usually an online merchant, and the fraudsters’ deception intends to remain undiscovered.
6 Most Common Ecommerce Fraud Types
Here are the most common eCommerce fraud types.
1. Credit card fraud
Credit card fraud is the type of fraud caused by using a credit or a debit card.
In the context of eCommerce credit card fraud, the fraudsters use the stolen credit card information to purchase from a merchant’s store.
There are many cases where fraudsters buy the stolen credit cards on the dark web and use the stolen card data to purchase a product or service.
The initial transaction defrauds the cardholder whose card was previously stolen.
Eventually, it also defrauds the store owner, who has to refund the purchase and sometimes pay a chargeback fee to the issuing bank.
For this reason, merchants who don’t proactively prevent payment frauds are losing money due to chargebacks, false positives, and operational inefficiencies.
2. Affiliate fraud
Affiliate fraud is an illegal online activity where fraudsters tend to generate affiliate commissions.
When it’s up to affiliate marketing, an online merchant pays a commission to affiliates for each sale that affiliates bring.
The merchants give a unique trackable URL to an affiliate that points customers to the merchant’s store.
When a customer comes through one of the affiliate links and purchases, the merchant gives the affiliate a commission for a referral.
The commission is usually returned as a percentage of the sale price.

In affiliate fraud, criminals deceive the system and defraud the merchant by using fake activities to generate commissions or increase the commissions’ total amount.
Usually, the most common form of affiliate fraud is “typosquatting,” where a fraudster registers domain names that match commonly mistyped versions of an actual online store’s URL.
Then, the fraudster redirects that domain name to the merchant’s website, including an affiliate link.
3. Chargeback fraud
In the online world where credit card transactions are something normal, a chargeback is an occurrence where a credit card provider makes a retailer refund a fraudulent or some disputed transaction.
In eCommerce, chargeback fraud occurs when an online customer purchases with their credit card, receive the product or service but then requests a refund from the credit card company, who pushes that through the issuing bank (also known as card issuer).

Also referred to as “friendly fraud,” this kind of fraud results in the payment processor demanding that the merchant refund the purchase amount to the issuing bank.
After demanding a chargeback, the online merchant needs to refund the purchase.
In a common situation of chargeback fraud, a customer purchases from an online store.
After receiving the products or services, the fraudster waits weeks or months to contact the bank and disputes the transaction, claiming the transaction as unauthorized or fraudulent.
The fraudsters usually hope that the merchant lacks the time and resources to disputing the claim or gives them the benefit of the doubt.
4. Phishing/account takeover
Most eCommerce merchants store customers’ personal and financial data as also as purchase history.
All of this may be a massive threat if you don’t protect your customers’ information adequately.
Cybercriminals may break into these accounts through simple phishing schemes.
One of the most common tactics is the fraudsters sending emails to trick the customers into sending personal data such as usernames and passwords of their accounts.
Fraudsters use it then to log into the customers’ accounts, steal them, and make those unauthorized purchases.
One of the common ways that customers are using to create accounts on eCommerce sites is social media logins. However, if social media information gets hacked, it can be devastating for the user.
What cybercriminals are also using are bots that are stealing confidential information, resulting in customers being plagued by the fallout of identity theft.
Account takeover fraud occurs when a human or bot uses the stolen account data to access customer accounts.
Once the fraudster gets access, they can steal customers’ other personal data or purchase products or services from their account.
Easy account takeover frauds on store damages brand reputations and can damage the trust of your customers forever.
The rise of non-financial credentials fraud is happening due to the dark web demand of stolen email addresses, social media accounts, passwords, and other personal information.
When a cybercriminal discovers the right combination of credentials, they can access and exploit many customers’ accounts.
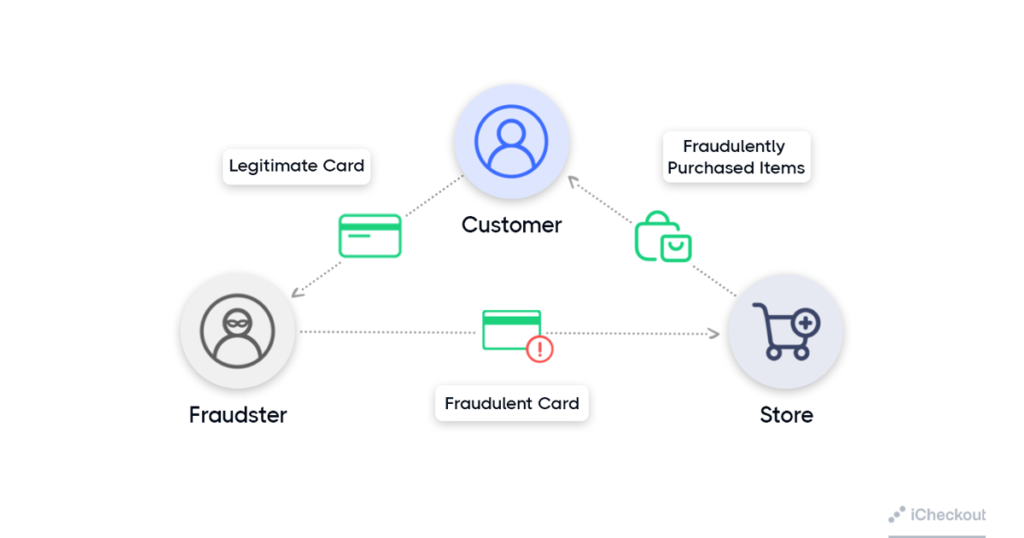
5. Triangulation fraud
Triangulation fraud consists of three steps to defraud online merchants.
First step: Fraudsters create a fake online storefront, usually the one that offers popular brand products at low prices.
The site’s only goal is stealing names, addresses, personal information, and credit card numbers from unsuspecting customers.
Second step: At this step, the fraudsters use the stolen customers’ addresses, passwords, and credit card numbers to visit a legit online store, buy exactly what the customer purchased from the fake one, and ship that product to the customer.
Third step: This is the step where the fraudsters use the stolen customers’ credit cards and personal data to make online purchases that they ship to themselves.
This type of fraud usually stays undiscovered for a longer period of time than other types of frauds.
That’s because the original purchase (from the fake site) raises no doubts on the victim’s part.
6. Interception fraud
Interception fraud is a type of fraud where fraudsters use the stolen credit card data to make online purchases, ship the products to the address on file for the credit card at checkout, and then intercept the package before it gets delivered.
For example, a criminal may visit an online store and use stolen credentials, credit card, and shipping details to purchase the product.
After they complete the transaction, the fraudsters call customer service before the item gets sent, and they change the delivery address to their desired address.
Interception fraud is usually done to obtain products that the fraudsters are reselling later.
9 eCommerce fraud prevention best practices
1. Enable fraud protection tools
Depending on the payment processors you use to accept online transactions through your store, you may have access to some of the fraud prevention tools.
Some of those tools are free, but even if there is a monthly charge to pay for it, it’s worth it.
In the long run, it’s much better to pay a minimal monthly cost for the tool rather than later paying thousands of dollars for fees and losses.
However, the filters below should be enabled you to help you reduce fraudulent attacks and collect as much information as you can:
- Card Verification Value (CVV) filter – it requires a customer to enter the 3- or 4- digit code from the back of their card.
- Address Verification filter – verify if the billing address and zip code match with what the issuing bank has on file.
- Velocity filter – a filter that’s preventing card runners from testing their cards on your accounts.
- Unmatched Refunds filter – stops refunds from going back to cards that didn’t have the original sales charged to them.
2. Maintain PCI compliance on your store
Any merchant storing or processing credit or debit card information must comply with the PCI standards for compliance.
PCI standards are managed and developed by the PCI SSC (Security Standards Council).
These standards were established to ensure customers’ credit card data security within merchants’ payment systems, including eCommerce websites.

Regardless of the payment methods you accept, PCI compliance is an ongoing process for every business that accepts credit and debit cards.
For example, if you operate a SaaS-based eCommerce store, your platform will typically provide this compliance.
The Payment Card Industry Security Standard Council (or PCI in short), in partnership with global brands like Visa and MasterCard, created rules to protect businesses on the Internet and keep customers’ data safe.
3. Identify Suspicious Signs of Fraud
Differences in a customer’s online identity and their personal identity empower merchant security companies to identify the potential of fraud.
The most common signs of fraud include:
Card Testing Fraud: Card testing fraud happens when fraudsters make small fraudulent purchases on an eCommerce store to verify details of the stolen credit card.
Small orders help fraudsters to avoid fraud detection and ensure their stolen credit card data is correct before making larger purchases.

These small transactions made in quick succession, including a high rate of authorization failures or card verification value, indicate card testing fraud.
To prevent card testing fraud, merchants detection of orders that have an AVS mismatch or CVV mismatch, or in case the orders don’t match a customer’s specific geolocation or online order behavior.
Payment Fraud: Payment fraud is committed when the fraudsters make purchases using a stolen credit card data. Payment fraud usually results in fraud chargebacks for merchants.
To prevent those fraud chargebacks, merchants should flag suspicious activities by looking at various data points.
Distance and difference between a customer’s shipping address, billing address, and IP address, especially if high-value products are being purchased, and payment attributes are all valuable points to the survey.
Friendly Fraud – Friendly fraud happens when a customer makes an online order and then disputes it.
To identify friendly fraud, you need to check the customer’s dispute with their order history, shipping and billing information, and refund policy.
Merchants can prevent friendly fraud using custom rules that flag order disputes that are repeating and are linked to the same email, phone number, card number, or shipping address.
Promotion fraud: To take advantage of promotions, fraudsters are creating fake accounts or do account takeovers to steal promo codes and discounts.
There are two methods that merchants can use to stop this kind of fraud. Merchants can prevent fake account creation from the same device and IP address.
Or they can survey new accounts and look for suspicious behavior using behavioral analytics and require those accounts to verify their identity before claiming a promotion.
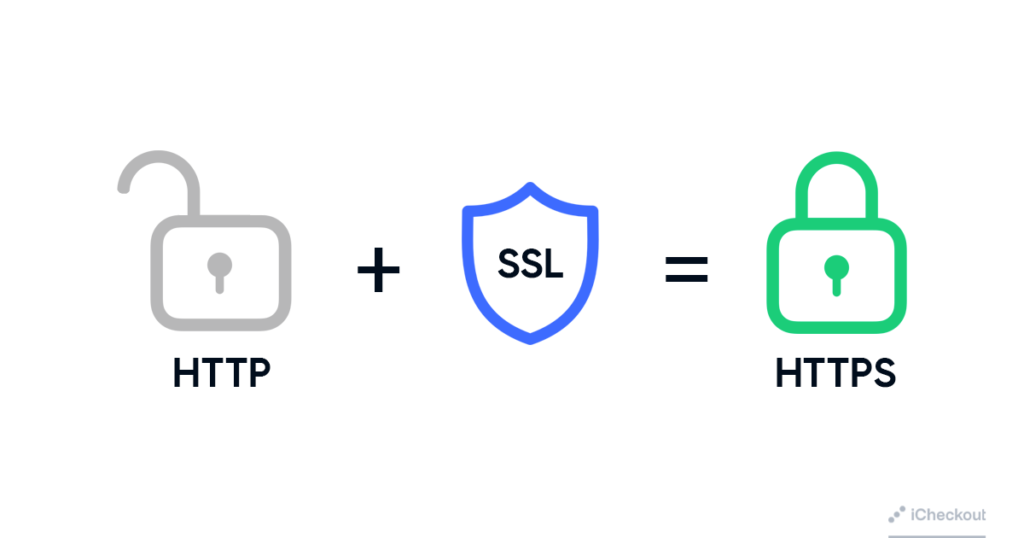
4. Install SSL and use HTTPS
HTTPS is the version of the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) but secure one.
This protocol is generally used for sending the data between a web browser and your online store.
What HTTPS does is that encrypts customers’ data to protect sensitive information, such as name, customers’ addresses, and credit card details.
Using HTTPS, you prevent your store from having its transactions distributed by cybercriminals and fraudsters.
By buying an SSL certificate and installing it, you get HTTPS.
Also when it comes to eCommerce SEO, an SSL certificate is what Google sees as a positive ranking factor.
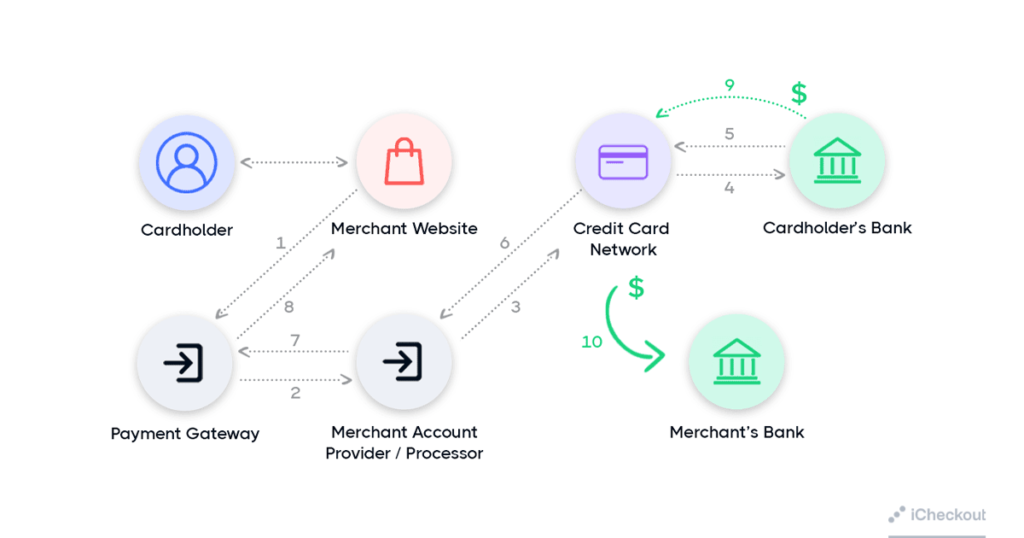
5. Use 3D Secure 2.0
A fraudulent chargeback can happen if a consumer’s payment information gets stolen or in case the consumer disputes a valid purchase.
What’s not so great is that merchants often have to carry this cost.
Implementing 3D Secure can help you shift liability from yourself to the card issuer.
3D Secure 2.0 enables this extra protection helping you to reduce the unnecessary friction in the checkout process.
Here’s how it works:

Also, accepting local payment methods such as bank transfers can also limit your vulnerability and liability to payment card chargebacks.
6. Implement Invisible Verification
More than half of the internet traffic originates from some kind of automated program called bots.
We’re all familiar with the display of letters and squiggly lines that websites use to make us prove we are humans.
New reCAPTCHA technologies are making this process effortless and invisible for your customers.
Using reCAPTCHA, you can choose whether your customers should check a box or determine if the user is human without taking any particular actions at all.
7. Require Card Verification Value (CVV) numbers for the purchases
The three or four-digit security code on the back of customers’ credit and debit cards is called the Card Verification Value (CVV) number or Card Security Code (CSC).
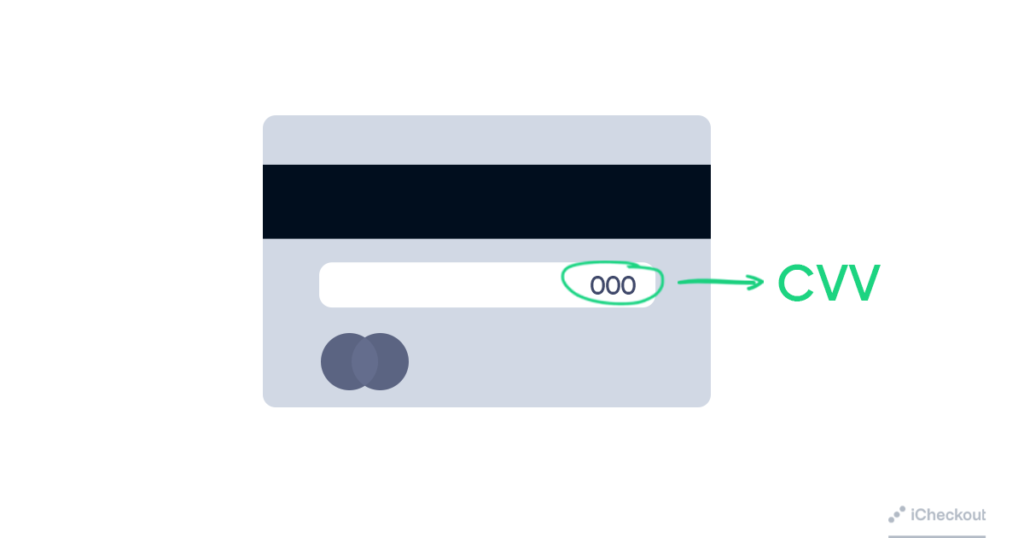
By demanding the CVV code for each transaction that your customers do, you ensure that they have the credit card in their possession.
This method helps you keep your store safe, and it reduces fraud.
8. Avoid collecting sensitive customers’ data
One way to protect your store and your customers’ data from frauds is to collect and store as little data as possible because fraudsters can’t get from you something that you don’t have.
Collect only the data that you need to complete a transaction and ship the product to the customer.
It’s good not to collect Social Security numbers, birth dates, and other sensitive customer data.
9. Keep your tool up-to-date
Cybercriminals usually use tools to detect sites with not updated apps and plugins.
By keeping your store and backend software updated with the latest security versions, you reduce the risk of vulnerabilities to potential hackers.
On the other side, you should install and regularly update anti-spyware and anti-malware software for your businesses.
The free antivirus software just isn’t enough to protect your systems from being exploited.
10. Use a reliable third-party payment processor
Outsourcing fraud prevention and security to a third-party payment processor are one of the easiest and also safest ways to eCommerce fraud prevention.
Third-party payment processors usually manage the customers’ chargebacks, security compliance, and data storage, keeping their data safe.
What a third-party payment processor can do is to keep customers’ private data secure, which can cut the number of eCommerce fraud attacks.
The safety of customers is the payment processor providers’ top priority, especially if customers have their credit card details saved in their accounts.
Educate your customers to prevent fraud attacks
It’s easier to fight fraud and prevent it when you know what you’re up against. Cybercriminals and fraudsters are always searching for new ways to threaten your payment environment.
Sometimes they go that far as to hack into a smart appliance, such as a refrigerator, to get your customers’ personal details or the account information that will allow them to gain something for free at your or your customers’ expense.
Implementing these best practices will help you secure your store and will improve your eCommerce fraud prevention.
In case you need help to securely accept payments for your online business, look for safe payment gateway solutions or some fraud prevention tools to keep your business safe.
Now it’s up to you to implement it, and what’s important is to have a secure checkout process because all the payments are happening there.
What’s great is to also use third-party checkout plugins if you don’t want to worry about the security on the checkout.
That’s why we created iCheckout – a better-converting, frictionless one-page checkout that will keep you and your customers purchasing safe.
85% of online purchases are made using mobiles.
That’s why all customer interactions in iCheckout are masterfully crafted with a mobile-first approach – to provide the smoothest checkout experience of all time.
With thousands of eCommerce elites, we’ve built the ultimate checkout process that redefines the purchasing experience while keeping it secure, easy, and seamless.
iCheckout helps you leverage the power of social proof and reviews at every step of the checkout process and increase your revenue by 21% through automatic discounts and the smartest upsells you have ever seen.
Using iCheckout on your store, customers shouldn’t spend more than 25 seconds on the checkout page.
You are two clicks away from setting up the CRO tool that will skyrocket your business – literally.
Things like these shouldn’t be hardcoded, and we are here to help you save time and focus on one thing that truly matters – scaling.
iCheckout is about to release the beta soon, so you can test the tool and see how it fits your eCommerce needs.
Join our waitlist, and be among the first beta users when iCheckout gets live!




